

The eardrum is composed of connective tissue and is covered by skin on the outer side and a mucous membrane on the inner side. It separates the outer ear from the middle ear.
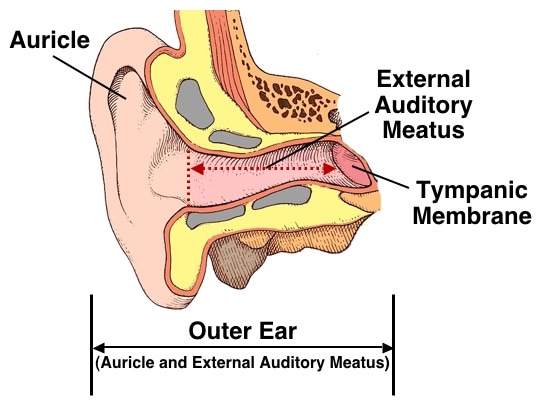
It is approximately 2.5 centimeters long, with the outer one-third made of elastic cartilage and the inner two-thirds composed of bone. External Auditory Canal: The external auditory canal, also called the meatus, is a curved tube that connects the pinna to the tympanic membrane.Its primary function is to collect sound waves from the environment and direct them into the ear canal. The pinna has fine hairs and glands that secrete wax. It has a curved shape and is composed of cartilage covered with skin. Pinna: The pinna, also known as the auricle, is the visible outermost part of the ear.The outer ear consists of several parts that contribute to its overall anatomy and function. The three anatomical regions of the ear are – the outer ear, the middle ear and the inner ear. Understanding the structure and mechanisms of the ear is important for comprehending the process of hearing and its integration with the central auditory pathways of the brain. The ear converts sound waves into electrical impulses, which are then processed by the brain for interpretation. Its structure consists of the outer ear, middle ear, and inner ear, with the cochlea being the primary organ of hearing. In summary, the ear is a complex organ responsible for both hearing and maintaining balance.The structure and functioning of the ear are essential for normal hearing, involving the coordinated interplay of the outer, middle, and inner ear. The human ear has a hearing range of 20 to 20,000 Hz through air conduction, while bone conduction can transmit much higher frequencies. Hearing is a vital sense that allows us to perceive and interpret sounds, communicate, and detect environmental signals.The specific vibration patterns produced by a sound source, such as a human speaker, are converted into auditory signals by the ear. When sound waves enter the ear, they cause the particles of the medium to vibrate parallel to the direction of the sound wave, creating compressions and refractions. Sound is a mechanical energy wave that travels through various mediums, such as air or other physical substances. The process of hearing involves the transduction of sound waves into electrochemical impulses.This information is essential for maintaining equilibrium and coordinating movements. It contains the vestibular labyrinth, which consists of fluid-filled canals and chambers that detect the position of the head and the body in relation to gravity. In addition to hearing, the inner ear also plays a crucial role in maintaining balance.These impulses are then transmitted to the brain through the auditory nerve for further processing and interpretation. When the vibrations from the middle ear reach the cochlea, the hair cells detect the movements and convert them into electrical impulses. The cochlea is filled with fluid and contains tiny hair cells that are sensitive to vibrations. It contains the cochlea, a snail-shaped structure that is the main organ of hearing. The inner ear is the innermost part of the ear and is responsible for converting sound waves into electrical signals that can be interpreted by the brain.These bones amplify and transmit the vibrations to the inner ear.

The vibrations from the eardrum are then transmitted to three small bones called the ossicles: the malleus (hammer), incus (anvil), and stapes (stirrup). It contains the eardrum, a thin membrane that vibrates in response to sound waves. The middle ear is located between the outer ear and the inner ear.The sound waves enter the ear canal and travel towards the middle ear. It consists of the pinna, which is the external part of the ear, and the ear canal. The outer ear is the visible part of the ear that collects sound waves from the environment.It is a complex structure consisting of three main sections: the outer ear, middle ear, and inner ear. The ear is one of the five sensory organs of the human body and serves the primary functions of hearing and maintaining balance.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
